Beyond the bridge: How the definition of infrastructure is expanding.
Illustrative example
Stage 1: Traditional infrastructure
Infrastructure begins with physical assets— durable, capital-intensive structures like bridges, roads, and tunnels, valued for their capacity and reliability.
1
Traditional infrastructure
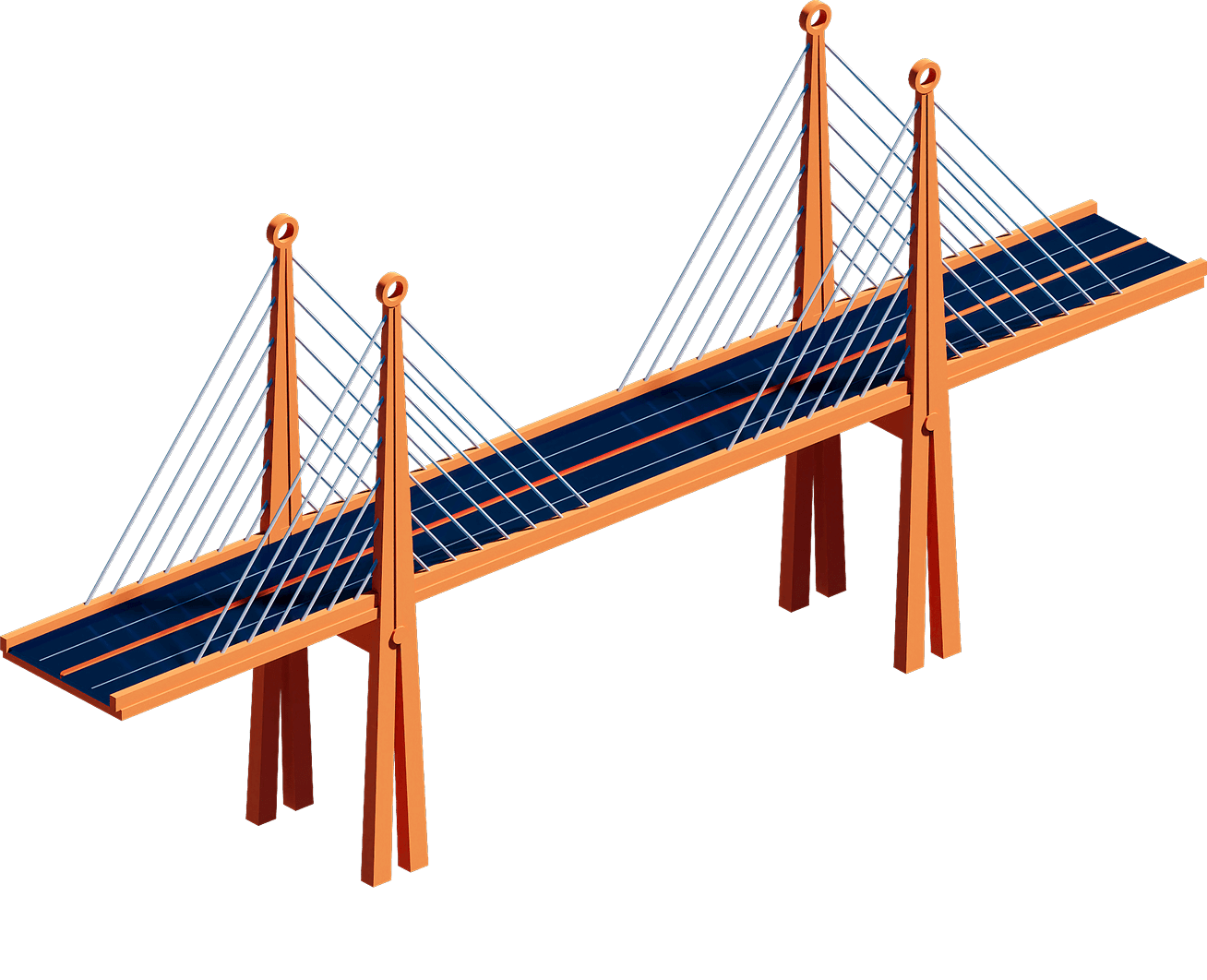

Bridge structure: Concrete, steel, and road deck form the backbone of bridges—structures that embody the traditional fixed, physical assets built for durability and capacity
McKinsey & Company

2
Infrastructure with services
3
Infrastructure with technology
4
Infrastructure ecosystem

Prev

Next
1
Traditional infrastructure
Stage 2: Infrastructure with services
The definition expands to include operations and maintenance—toll collection, inspection, repair, and resurfacing—highlighting infrastructure as an ongoing service system, not just a one-time construction project.
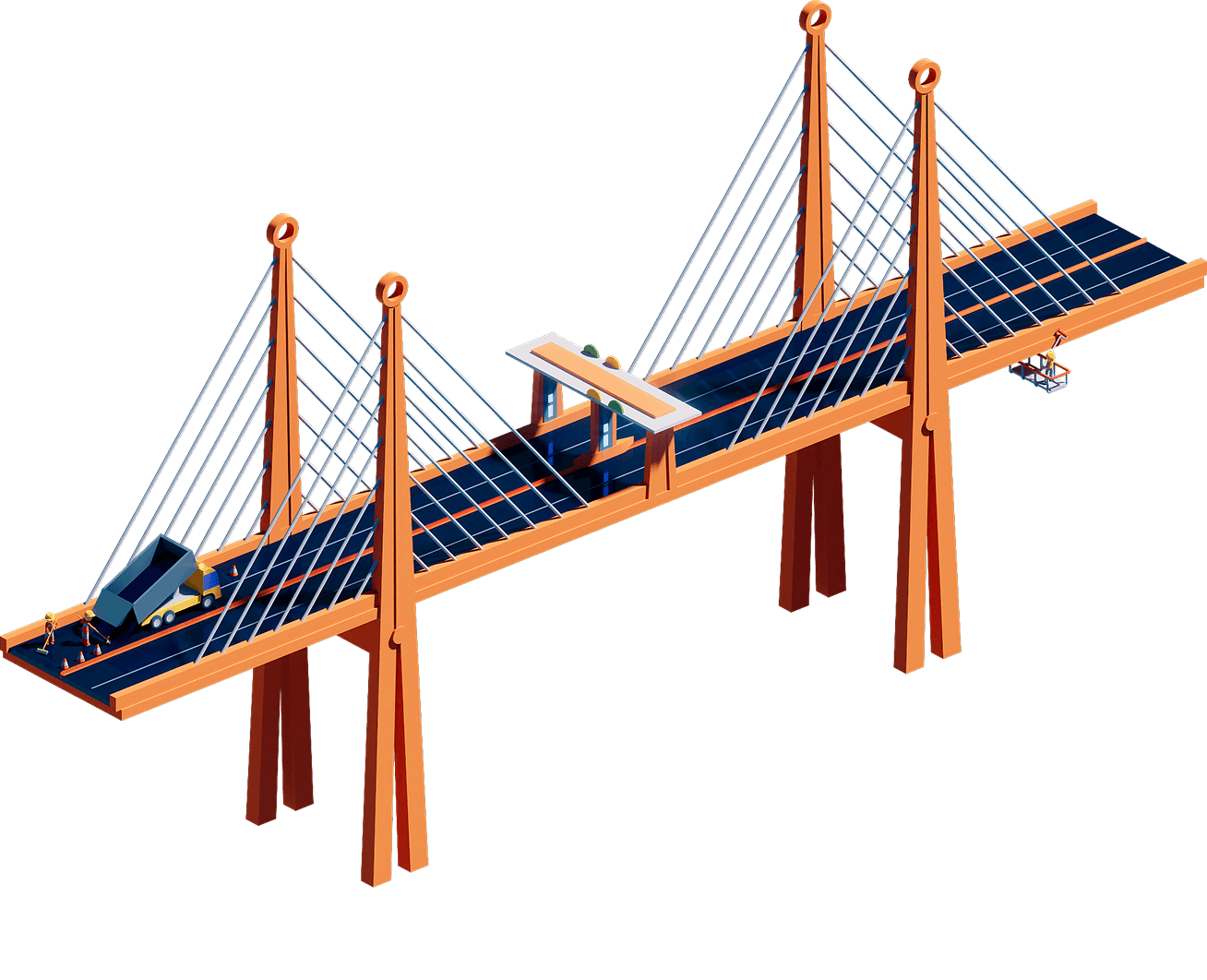

Structural inspection and repair: Regular monitoring and fixing of structural elements to ensure safety and extend lifespan
Traditional toll booth: Manual or semi-automated toll collection services that fund operations and regulate use


Painting and resurfacing: Routine upkeep to maintain road quality and protect against wear from weather and heavy traffic
2
Infrastructure with services
1
Traditional infrastructure
Stage 3: Infrastructure with technology
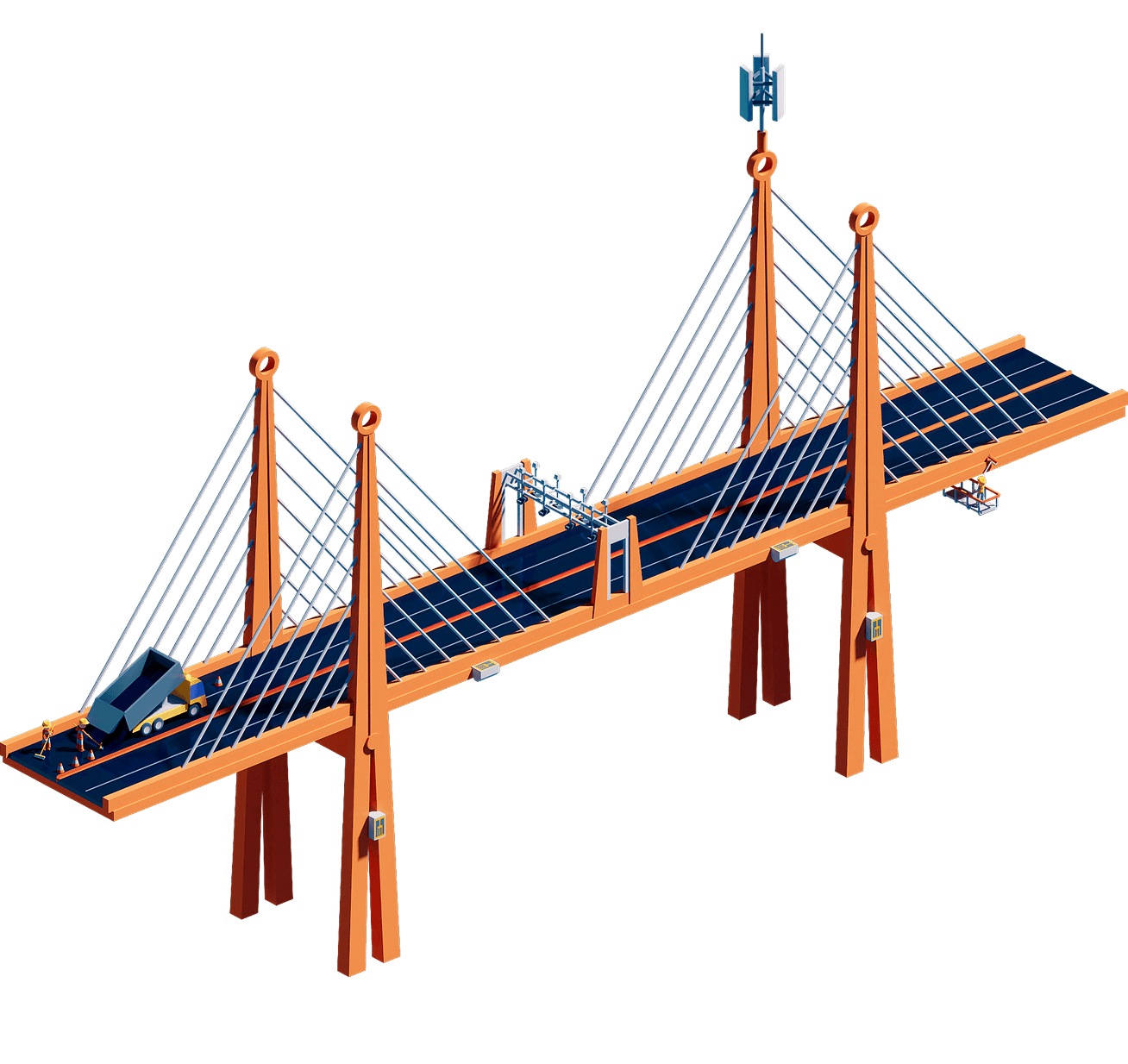
With digital layers, infrastructure becomes “smart.” Sensors, automation, and connectivity enable predictive maintenance, dynamic tolling, and advanced mobility use cases such as autonomous vehicles. Infrastructure begins to generate data and intelligence.
5G towers: Connectivity that supports autonomous vehicles and enables fast, reliable communication between infrastructure and users

IoT strain gauges: Embedded sensors that track stress and wear in real time, enabling predictive maintenance
Dynamic tolling and license-plate OCR: Automated toll systems that adjust pricing based on congestion and scan vehicles seamlessly

2
Infrastructure with services
1
Traditional infrastructure
3
Infrastructure with technology
Stage 4: Infrastructure ecosystem
Finally, infrastructure is seen as part of an integrated ecosystem. The bridge links to renewable energy systems, electric vehicle charging, logistics hubs, ports, and airports. Infrastructure now underpins entire networks of energy, mobility, and commerce.
Power grid for EV charging stations: Clean energy networks linked �to transport infrastructure, supporting the shift to electrification

Airports: Global logistics nodes that connect air transport with ground networks, facilitating international mobility and commerce
Warehouses: Logistics hubs that connect bridges to supply chains and regional commerce

3
Infrastructure with technology
2
Infrastructure with services
1
Traditional infrastructure
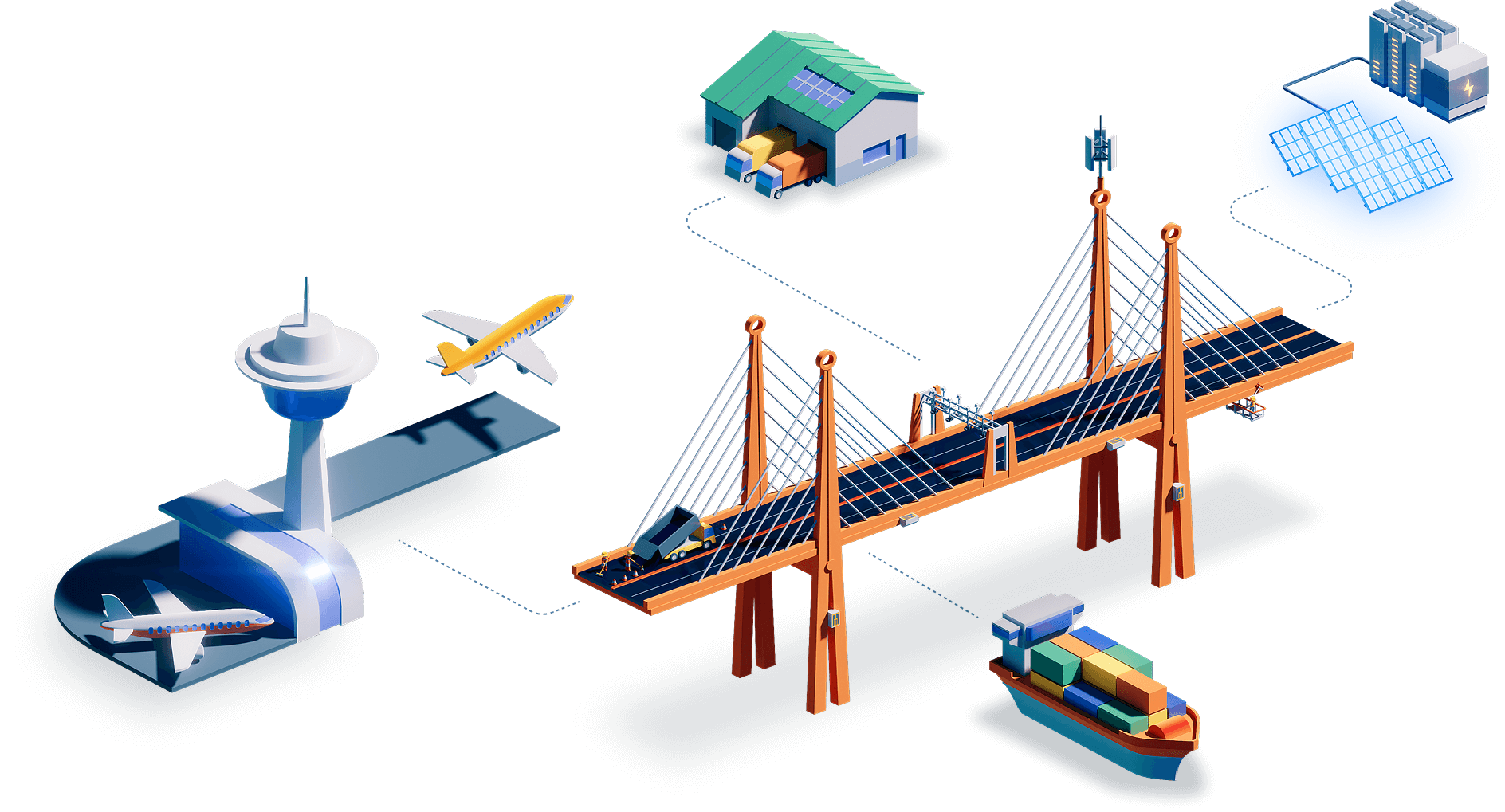


Shipping: Integration with ports and maritime trade routes, enabling global goods movement
4
Infrastructure ecosystem